Permalinks, or "permanent links," have a strong impact on website URLs. It influences user experience and impacts SEO performance.
All of the primary components such as the full URL, domain, subdomain, and slug present in a permalink are important for your website’s organic visibility.
Hence, you should choose an SEO-friendly permalink structure that search engines and users can easily crawl and index.
What is a Permalink?
A permalink, or "persistent URL," is a fixed URL that directs users to a specific page or post on a website.
Acting as a "persistent identifier," it includes essential components like the page slug, which helps make the link human-readable and SEO-friendly.
Good permalinks are clear, clean URLs that include the category and post name, making them more clickable and understandable.
Bad permalinks, on the other hand, include random characters or lack context, which can harm user experience and SEO.
Content management systems use HTML to create permalink structures that enhance navigation and improve URL structure for search engines.
Example of a Permalink
Here is a well-structured permalink example:
https://growth.toolzbuy.com/udemy_cloud/keyword-research-tool
In this permalink:
- "https://growth.toolzbuy.com/udemy_cloud" is the domain and subdomain, establishing the main website location.
- "/keyword-research-tool" is the page slug, which is human-readable, specific, and relevant to the page content.
The above URL structure is a fine example of a clean and SEO-friendly permalink.
It’s clear, descriptive, and gives users and search engines an immediate idea of what the page is about, enhancing both clickability and SEO.
How to Create an SEO-Friendly Permalink
Here are the best practices to follow for creating search-optimized permalinks:
Describe the Content and Include Keywords
Use keyword-focused slugs that clearly describe your content. Always remember to place the primary keyword within the URL, but avoid overloading it with repetitive terms.
For instance, at SEOptimer we only use the primary keyword in the page's URL. Here is an example from our post targeting the keyword "ideal client profile."
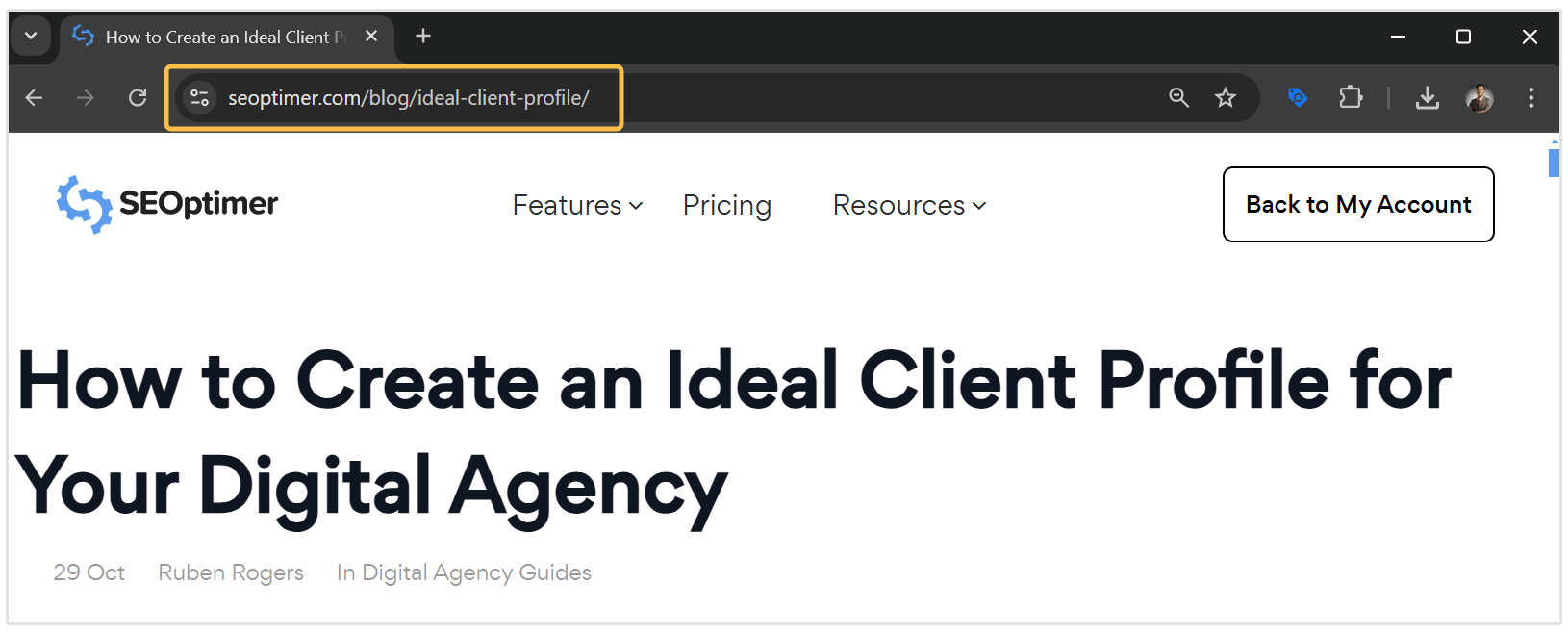
Using your seed search term helps search engines, and users understand what the page is about and improves search visibility.
Every single piece of content that you publish should have the primary target keyword in its URL.
- Matthew Woodward, Founder of SearchLogistics
Also, use keywords once in the URL to avoid keyword stuffing. Overuse can make the URL look spammy and may hurt SEO.
Use Hyphens Instead of Underscores
For SEO purposes, separate words with hyphens rather than underscores.
Hyphens are more readable for both users and search engines.
Just as an example, which of these permalinks read easier, the one with hypens or underscores:
- www.seoptimer.com/blog/seo-best-practices
- www.seoptimer.com/blog/seo_best_practices
Furthermore, when words are separated by hyphens, search engines recognize each word in the URL independently, aiding in proper indexing and visibility.
In contrast, URLs with underscores cause search engines to treat the entire string as a single term, which can reduce clarity and affect how the page ranks for specific keywords.
Keep a Short and Simple URL Structure
When URLs are clear and direct, users can quickly understand the page's purpose and location on the site.
You should avoid adding unnecessary directories, and keep your URL path as short and simple as possible.
Short URLs are easier to remember, share, and type. They also perform better on mobile devices, where screen space is limited.
Avoid Using Dates and Numbers
Unless date specificity is essential, avoid including dates in URLs. This helps keep content evergreen, meaning that it won’t appear outdated to users or search engines over time.
For instance, our blog post on "How SEO will Change in 2025" deals with a specific timeperiod, so it would make sense to use the permalink "www.seoptimer.com/blog/seo-2025".
However, if we were talking about a post on general SEO best practices, you would want to avoid adding any dates to the permalink.
Also, excluding numbers, such as versions or item counts, keeps URLs adaptable. This prevents the need to update URLs if the content changes or expands.
For instance, we had a blog post titled "10 Ways to Generate SEO Leads", however, we decided to refresh the content and add additional tactics, so the title now reads "17 Tactics Agencies Use to Get SEO Leads & Clients".

Luckily the permalink for the original post was "seo-leads" so we were able to stick to that when we refreshed the content.
Imagine if we used "10-ways-seo-leads" as the permalink for the original post, we'd have to create an entirely new page with a new URL, meaning we would have lost all of the original page's backlinks and authority.
Utilize Categories Thoughtfully
When applicable, organize URLs with categories to give a sense of hierarchy.
For instance, many popular websites use the "/blog/category/post-name" format to clarify content organization, while avoiding unnecessary layers.
Avoid UTM Tracking and Dynamic URLs
Keep tracking parameters like UTM tracking codes out of permanent URLs. These are better suited for campaign tracking rather than direct user navigation.
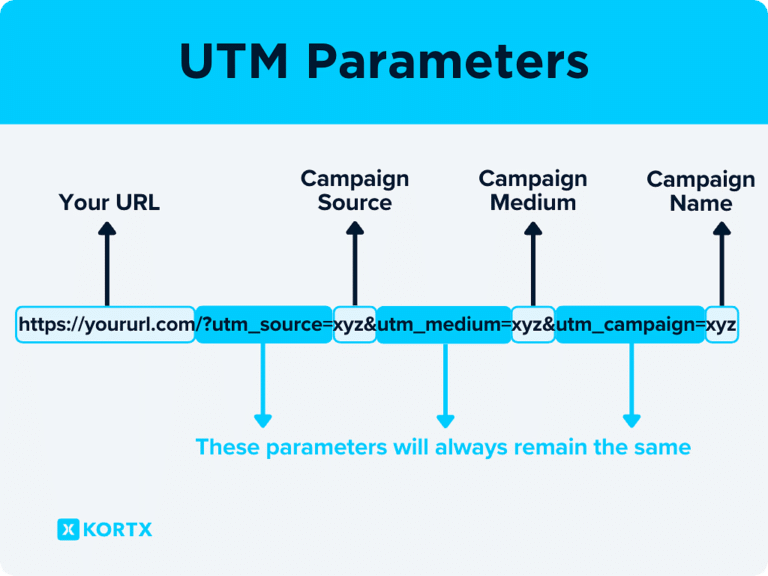
Also, avoid dynamic URLs with query strings, which can lead to different versions of the same content and cause duplicate content issues.
According to Google, URLs with multiple parameters can cause problems for crawlers.
Overly complex URLs, especially those containing multiple parameters, can cause problems for crawlers by creating unnecessarily high numbers of URLs that point to identical or similar content on your site.
As a result, Googlebot may consume much more bandwidth than necessary, or may be unable to completely index all the content on your site.
- Google Search Central
Remove Special Characters
Special characters make URLs appear cluttered and make them especially difficult to read. Search engines prioritize SEO-friendly permalinks that are easy to parse.
Clean URLs by removing special characters, as they can complicate readability and indexing for search engines.
Some examples of special characters include:
- #
- < and >
- %
- { and }
- [ and ]
Use a Subfolder for Organized Structure
Organize pages under relevant subfolders, such as /blog/seo-tips, if necessary, instead of scattering content across unstructured links.
When content is organized within a logical folder structure, it signals to search engines how different pages relate to each other, enhancing your site's relevance in specific topic areas.
How to Customize Permalink in WordPress
Login to your WordPress dashboard and point the cursor to Settings. You will see a number of options, choose permalinks.
Here, you will see different permalink structures, including the %postname% tag, which is the most SEO-friendly option among them.
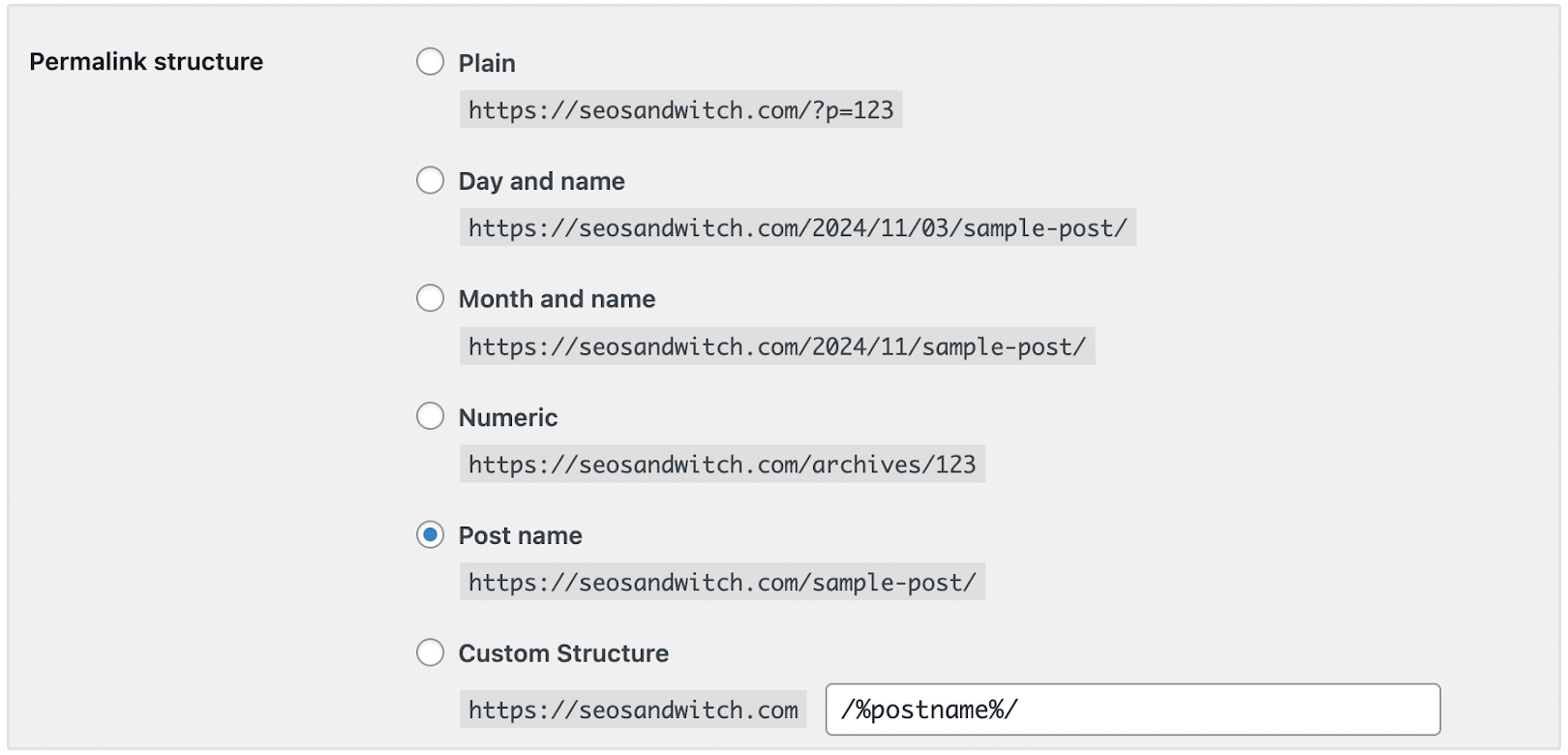
Now, select the Post name option, which displays the full URL with the post’s title to help your posts rank higher in search engines.
After selecting the Post name option, click Save Changes.
Customizing permalinks is very important for readability and search engine optimization, helping your content reach a broader audience effectively.
What is the Difference Between a URL and a Permalink?
The primary difference between a URL and a permalink is that a URL can be permanent or temporary but a permalink is always permanent.
A URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is the general address of any webpage or resource on the internet, serving as the clickable link that directs users to a specific location.
URLs can be used for various purposes, such as linking to internal or external websites, and may change or be updated over time with redirects.
A permalink is a specific type of URL designed to be permanent, leading directly to a particular piece of content, like a blog post or article.
Unlike regular links that may change as websites evolve, permalinks serve as unique URLs meant to stay consistent, making them ideal for content that requires a stable, organizational link structure.
Permalinks are carefully crafted to be readable and memorable, supporting direct links without the risk of frequent redirects or address changes.
Should You Change a Permalink Once Created?
Once a permalink is created, changing it can disrupt existing links, leading to broken links that negatively impact SEO.
Search engines rely on stable URLs to index and refer to your content. If changing a permalink is necessary, such as for SEO improvements or brand consistency, set up a 301 redirect from the old URL to the new one.
Redirects ensure visitors and search engines are directed to the correct page, preserving traffic and search rankings. Ideally, plan and set permalinks thoughtfully from the start to avoid these issues.
Conclusion
Crafting SEO-friendly URL slugs helps enhance visibility and maintain SEO rankings.
Well-optimized and unique permalinks should be shorter, in lowercase, with keywords, and without special characters.
And, wherever you need to change your permalink, you can do that by using proper 301 redirects to keep your website’s organic positions safe.